ULNOLUNATE ABUTMENT SYNDROME
Clinical information: Pain and swelling at wrist joint.
Findings:
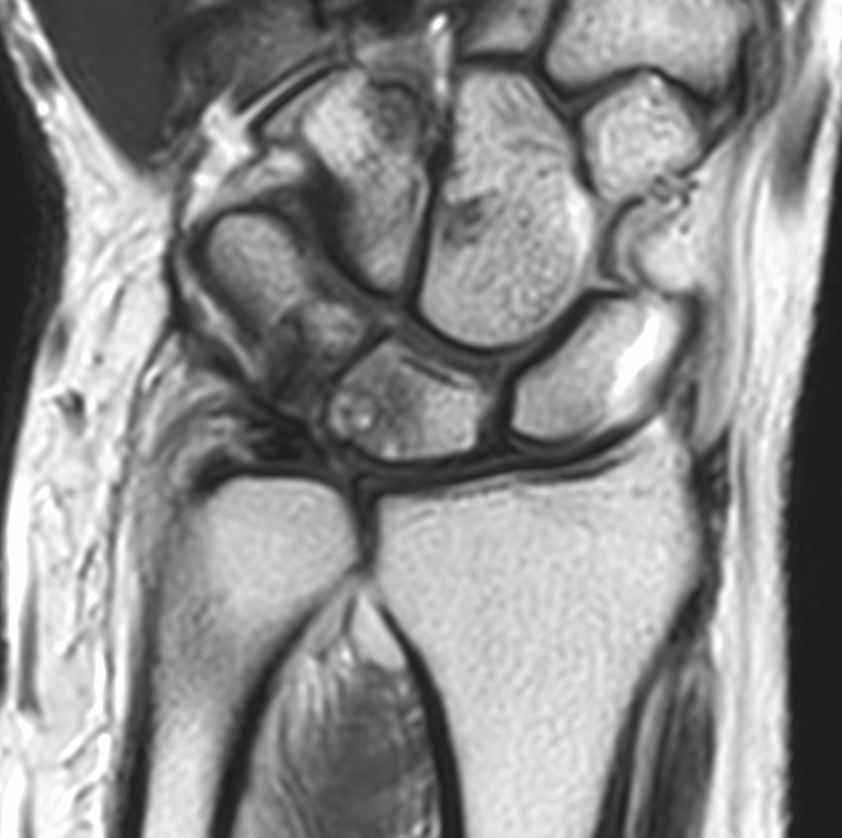
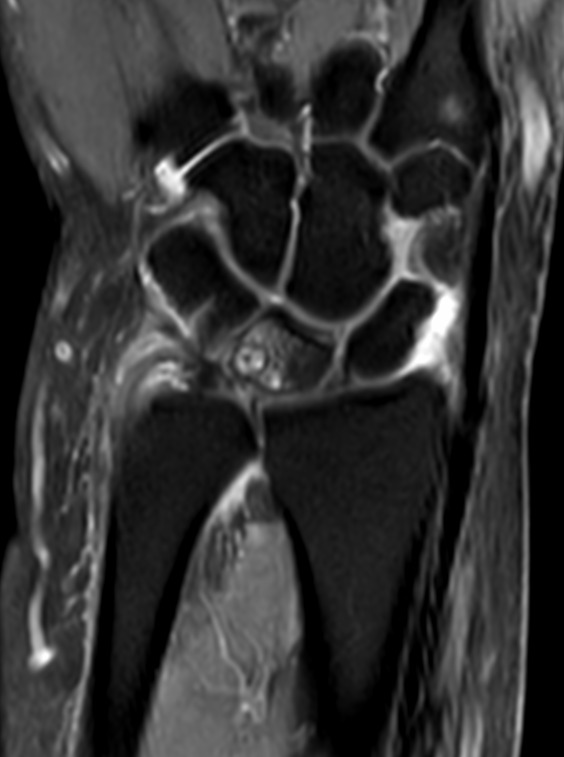
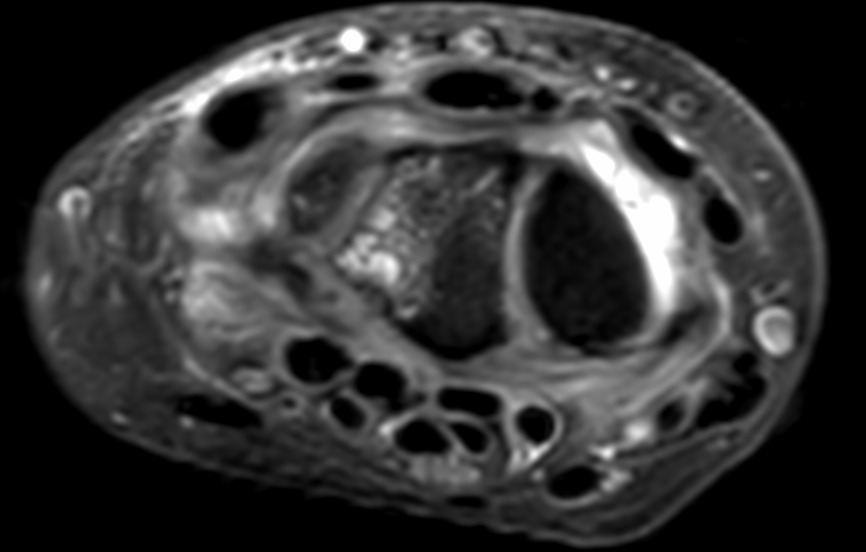
Few subarticular erosions with marrow edema and cyst formation are noted at the proximal ulnar aspect of lunate and proximal radial aspect of the triquetral bone.
No evidence of overlying soft tissue/ collection.
There is subtle hyperintense signal in the meniscal homologue of TFCC which may represent intrasubstance degeneration.
Subtle subchondral marrow edema also noted at lower end of ulna.
There is mild synovial thickening with fluid involving the radiocarpal, ulnocarpal and distal radioulnar joints.
No significant positive ulnar variance.
Findings are suggestive of ulnolunate abutment syndrome.
Discussion:
Ulnar impaction syndrome, also known as ulnar abutment or ulnocarpal impaction or loading, is a painful degenerative wrist condition caused by the ulnar head impacting upon the ulnar-sided carpus with the injury to the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC).
Ulnar impaction syndrome most commonly presents in middle-aged patients.
Ulnar impaction syndrome is rare in the absence of such anatomic predispositions but can occur if there is excessive repeated loading of the ulnar-carpus in daily activity.
MR imaging is the investigation of choice in both the detection of early disease and characterization of more advanced disease. Can demonstrate the bone, cartilage and ligamentous features of the syndrome.